Microbial Ecology

The ME department studies the diversity and functions of microorganisms in natural and managed ecosystems. We focus on two major research areas:
- the role of microorganisms in biogeochemical cycles and greenhouse gas emission
- ecology and evolution of soil and plant-associated microorganisms
We use an interdisciplinary approach, combining microbiology, molecular biology, chemistry, modelling and computational methods to study the taxonomic and functional diversity of bacteria, archaea, fungi, yeasts and viruses. We closely collaborate with various national and international universities, institutes and diverse (industrial, societal) stakeholders.
Our goals are to advance the mechanistic understanding of the multipartite relationships between microorganisms and their environment, and to contribute to the development of new strategies for sustainable management of natural and man-made ecosystems. We are actively involved in each of the three NIOO-wide research themes:
- Biodiversity: with the development of new ‘omics technologies, we have become even more aware of the vast, yet largely unknown diversity of microorganisms in natural and managed ecosystems. The ME-department studies microbial diversity and functions in national long-term ecological field sites (LTERs) as well as internationally such as the Amazon forest, the Andes Mountains and the Galapagos Islands. We use an interdisciplinary approach to illuminate the ‘microbial dark matter’ and to understand its impact on ecosystem functioning. Key questions are how soil bacteria, fungi and plants communicate and interact. For soil and plant-associated viruses (including phages), we investigate their role as the guardians of biodiversity.
- Climate change: microorganisms are key drivers of global nutrient cycles, catalyzing the emission of greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide and methane. We integrate(meta)genomic, isotopic and biogeochemical approaches to: a) identify key microorganisms, genes and pathways involved in these processes, and, b) assess their distribution, functioning and controls in various ecosystems, including lakes, peatlands, forests and agricultural soils. The ME department adopts this knowledge to identify major indicators of environmental disturbance and to steer microbial communities to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable use of land: ME research has shown that microorganisms living on and inside plants are drivers of plant growth and health. To harness the largely unexplored functional diversity, we investigate how plants under stress recruit beneficial microorganisms for protection and how introduction or steering of soil and plant microbiomes can be used as a sustainable practice to minimize fertilizer and pesticide use. We developed the concept of microbiome ‘rewilding’, which posits that plant health can be improved by reinstating key members of the diverse (ancestral) microbiota that were lost through domestication. To this end, we go back to the centers of origin of the wild relatives of our crop species to identify the ‘missing microbes’ and their beneficial traits.
Facilities
Biogeochemical cycles
Functional ecology of microbial communities involved in biogeochemical cycles.
Microbial community ecology & environmental genomics
Farming soil microbial community linked to N and P (re)cycles to provide nutrients to plants, soil quality and N2O mitigation.

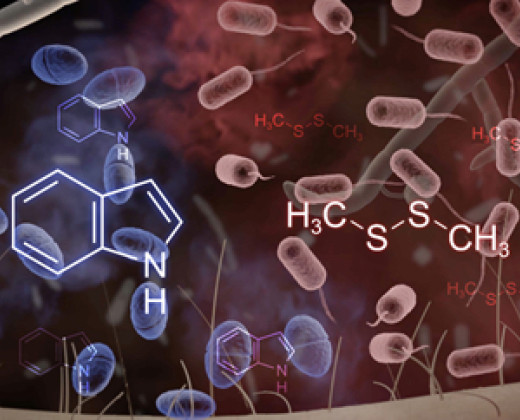
Chemical ecology
The chemical ecology of soil and plant-associated microbes
Virus ecology and evolution
Exploring the diversity, evolution and ecosystem impacts of plant-associated viruses.

Back to the Roots
Diversity & functioning of microbiomes of wild and domesticated plants.

Phyllosphere yeast ecology & genomics
Diversity, functions and interactions of phyllosphere yeasts associated with two plant species: the globally cultivated wheat and the endemic Scalesia species of the Galápagos Islands.
People
-
Prof. Jos Raaijmakers PhD
- Function
- Head of department

-
Prof. Paul Bodelier
- Function
- Senior Researcher

-
Dr. Viviane Cordovez
- Function
- Senior Researcher

-
Prof. dr. Paolina Garbeva
- Function
- Senior Researcher

-
Prof. dr. ir. Eiko Kuramae PhD
- Function
- Senior Researcher

-
Dr. Mark Zwart
- Function
- Senior Researcher

Events
Peer-reviewed publications
Microbial footprints of tomato domestication
Disentangling the molecular mechanisms of disease suppression by endophytic Flavobacterium sp. 98
Methane-oxidizing bacteria; “the gatekeepers of methane”
Unveiling the dominant role of soil pH in shaping nitrogen cycling microbial gene abundances
The effects of ecological interactions and distinct conjugation rates on the invasion of a conjugative plasmid in bacterial communities
Land Use Change Reshapes Climate-Driven Diversity Patterns of Tropical Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
Underground alarms
Biofertilizer induces soil disease suppression by activating pathogen suppressive protist taxa
Genomic insights into adaptative traits of phyllosphere yeasts
AHL quorum sensing regulates T6SS and volatiles production in rice root-colonizing Enterobacter asburiae AG129
Fungal Planet description sheets: 1868–1920
Acidotolerant soil nitrite oxidizer “Candidatus Nitrobacter laanbroekii” NHB1 alleviates constraints on growth of acidophilic soil ammonia oxidizers
Harnessing soil feedback from resistant bananas to suppress pathogens in susceptible varieties
Compartmentalized Homeostasis Drives High Bamboo Forest Productivity under Nutrient Imbalance
Hypoxia induces phenotypic and metabolic shifts in endophytic Flavobacterium sp. 98
The first checklist of fungi known for Honduras
Greater influence of eukaryotes on carbon degradation potentials than prokaryotes along an elevation gradient
The soil-plant-human gut microbiome axis into perspective
Fate of C and N from pretreated organic amendments in soil
Unveiling diversity and adaptations of the wild tomato Microbiome in their center of origin in the Ecuadorian Andes
Legume integration into rice cropping systems buffers topsoil functional potential against microbial diversity loss
Microbial engineering of soil structure
Essential and dispensable domains of DivIVA for walled growth in filamentous Actinomycetota
The novel GlcNAc 6-phosphate dehydratase NagS governs a metabolic checkpoint that controls nutrient signaling in Streptomyces
Spatial Prediction of Soil Microbial Enzyme Activities Using On-The-Go Vis–NIR Spectroscopy
Serotonin modulation of metabolism and stress response in Pseudomonas fluorescens
Catching cereal killers
Metagenome-based identification of functional traits of the black soldier fly gut microbiome associated with larval performance
Microbiome-Mediated Resistance of Wild Tomato to the Invasive Insect Prodiplosis longifila
Changing communities of ammonia-oxidizing Betaproteobacteria and Thaumarchaea at discrete vegetation zones along a hill slope grassland gradient
Aligning global mercury mitigation with climate action
Predicting rhizosphere-competence-related catabolic gene clusters in plant-associated bacteria with rhizoSMASH
Bio-organic fertilizer amendment helps suppress tomato bacterial wilt disease by improving aggregation and enhancing the pathogen inhibition capacity within micro-aggregates
NRPS gene dynamics in the wheat rhizoplane show increased proportion of viscosin NRPS genes of importance for root colonization during drought
Expansion of aerobic methanotrophy to the phylum of Actinomycetota and its environmental implications
Living Together Apart
Phosphate-cycling activity of the soil microbiome in response to the recycled phosphates struvite and vivianite
Linalool-triggered plant-soil feedback drives defense adaptation in dense maize plantings
Born to rewild
Global hotspots of mycorrhizal fungal richness are poorly protected
Periodic bioinoculations enhance soil aggregate stability through species-specific effects and interactions with the native microbiota
Synergy between AMF and accompanying microbiome enriched with PGPB enhances root development and microbiome dynamics
Genome mining based on transcriptional regulatory networks uncovers a novel locus involved in desferrioxamine biosynthesis
Exometabolome of Pantoea targets pathogen associated scytalone dehydratase and XopQ for suppression of foliar blast and bacterial blight in rice
Pigeon pea-mediated soil microbial shifts improve agroecosystem multifunctionality in long-term maize–palisade grass intercropping
Nematodes vector bacteriophages in compost and soil
Harnessing the phyllosphere microbiota of wild foxtail millet for designing beneficial cross-kingdom synthetic communities
Herbivory-induced green leaf volatiles increase plant performance through jasmonate-dependent plant–soil feedbacks
Foliar infections by Botrytis cinerea modulate the tomato root volatilome and microbiome
Biomimetic Total Synthesis and Paired Omics Identify an Intermolecular Diels-Alder Reaction as the Key Step in Lugdunomycin Biosynthesis
Synergistic interaction of phosphate nanoparticles from fish by-products and phosphate-solubilizing bacterial consortium on maize growth and phosphorus cycling
A blueprint for contemporary studies of microbiomes
Soil pH determines the shift of key microbial energy metabolic pathways associated with soil nutrient cycle
Total synthesis, structure elucidation, and bioactivity evaluation of the cyclic lipopeptide natural product Paenilipoheptin A
First Report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 Causing Black Scurf on Solanum tuberosum cv. Superchola in Cotopaxi, Ecuador
Joint ventures in plant performance
Diversity and functional potential of the sorghum root microbiome to control Striga hermonthica
Exploring the Chemical Space of Paenibacillus NRPs and Discovery of Paenilipoheptin B
On the diversity of nematode antagonists in an agricultural soil, and their steerability by root-knot nematode density and cover crops
Domesticated rice alters the rhizosphere microbiome, reducing nitrogen fixation and increasing nitrous oxide emissions
Using problem formulation for an efficient, fit-for-purpose risk assessment of microbial plant protection products
Novel bacteriophages targeting wheat phyllosphere bacteria carry DNA modifications and single-strand breaks
Liming enhances the abundance and stability of nitrogen-cycling microbes: the buffering effect of long-term lime application
Harnessing the synergy of Urochloa brizantha and Amazonian Dark Earth microbiomes for enhanced pasture recovery
Spinach Seed Microbiome Characteristics Linked to Suppressiveness Against Globisporangium ultimum Damping-Off
Impact of long and short-term nutrient input on microbial nitrogen cycling communities
First report of Pectobacterium peruviense as the causal pathogen of blackleg and soft rot in Solanum tuberosum cv. Superchola in Cañar, Ecuador
Improved methane mitigation potential and modulated methane cycling microbial communities in arable soil by compost addition
Beyond methane consumption
Enhancement of production of pathogen-suppressing volatiles using amino acids
MIBiG 4.0
Differential response of subterranean microbiome to exogenous organic matter input in a cave ecosystem
Mode of application of sulfonated graphene modulated bioavailable heavy metal contents and microbial community composition in long-term heavy metal contaminated soil
Fungal Planet description sheets: 1697-1780
Metabolic coupling between soil aerobic methanotrophs and denitrifiers in rice paddy fields
Exploring microbial diversity and interactions for asbestos modifying properties
Enhancing cucumber plantlet growth and rhizosphere microbial communities with chitin and gelatin biostimulants
Beneficial soil fungi enhance tomato crop productivity and resistance to the leaf-mining pest Tuta absoluta in agronomic conditions
Shotgun metagenomic analysis reveals the diversity of PHA producer bacterial community and PHA synthase gene in Addis Ababa municipal solid waste disposal area ‘Qoshe’
Cover crop mixtures do not assemble markedly distinct soil microbiotas as compared to monocultures in a multilocation field experiment
Positive effect of carbohydrate-metabolizing bacteria determines increasing soil organic carbon during long-term fertilization and straw returning in the black soil region of China
Evaluating Mechanisms of Soil Microbiome Suppression of Striga Infection in Sorghum
Intentional summer flooding of an Avicennia germinans mangrove forest has a more direct effect on ammonia-oxidizing Betaproteobacteria than on Thaumarchaea
Exploring modes of microbial interactions with implications for methane cycling
The use of living labs to advance agro-ecological theory in the transition towards sustainable land use
Dairy effluent applications to a pasture enhance soil fertility and microbial activity without impacting soil bacterial and fungal community composition
The role of strigolactone structural diversity in the host specificity and control of Striga, a major constraint to sub-Saharan agriculture
Darwin’s expedition revisited to reveal the evolution of plant–microbe interactions on Galápagos
Exploring the temporal dynamics of a disease suppressive rhizo-microbiome in eggplants
Diverse bacterial consortia
Methane-cycling microbial communities from Amazon floodplains and upland forests respond differently to simulated climate change scenarios
Biological Characterization of Physostegia Chlorotic Mottle Virus, an Emergent Virus Infecting Vegetables in Diversified Production Systems
Microbial community dynamics during decomposition of insect exuviae and frass in soil
Effect of microplastic pollution on the gut microbiome of anecic and endogeic earthworms
Bacterial genomes recovered from litter’s metagenomes in Amazonian Dark Earths
Mix-method toolbox for monitoring greenhouse gas production and microbiome responses to soil amendments
Fungal Planet description sheets: 1614-1696
Why change a winning formula?
Enhanced surface colonisation and competition during bacterial adaptation to a fungus
C4 cereal and biofuel crop microbiomes
Redefining Ellisembia sensu stricto with a reassessment of related taxa in Sordariomycetes
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi originated from soils with a fertility gradient highlight a strong intraspecies functional variability
Cultivar governs plant response to inoculation with single isolates and the microbiome associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Comparison of distinctive diversities, co-occurrence patterns and potential ecological functions of microbial communities in heterogeneous soil areas in typical subtropical forests, southeast China
EuropaBON EBV workflow templates
Discovery and Derivatization of Tridecaptin Antibiotics with Altered Host Specificity and Enhanced Bioactivity
A Comparison of Different Protocols for the Extraction of Microbial DNA Inhabiting Synthetic Mars Simulant Soil
Harnessing regulatory networks in Actinobacteria for natural product discovery
Soil aggregate stability governs field greenhouse gas fluxes in agricultural soils
Unraveling the impact of protein hydrolysates on rhizosphere microbial communities
Impact of insect herbivory and microbial inoculants on the rhizosphere microbiome and volatilome
The soil microbiome modulates the sorghum root metabolome and cellular traits with a concomitant reduction of Striga infection
Stem decomposition of temperate tree species is determined by stem traits and fungal community composition during early stem decay





