News
Search results
-
Micro-organisms too can cooperate and rewild
From insignificant individual cells to a rich community full of cooperation. That is how our understanding of the micro world of bacteria, fungi and other microscopic organisms has developed over the past two decades. This “microbiome” that exists on leaves and roots, for example, and in the gut and soil, has an enormous impact on the environment. Researchers at the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) are looking at functions such as the “consumption” of greenhouse gases, communication through scent and assistance to endangered plants.
-
Long-term nest box research offers insight into trends in nature
Great tits can't complain about a lack of attention. The Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) has hung nearly two thousand nesting boxes throughout the Netherlands for this “model species”. For seven decades researchers have been following the ups and downs of these songbirds. This makes it the longest-running study in the world of individually recognisable animals. The family trees, caterpillar peaks and breeding successes outline the development of climate change, acid rain and adaptation to a changing world.
-
Data breach discovered at the KNAW
On 24 November, the KNAW discovered a data breach caused by a phishing email. From 17 November onwards, a hacker had access to the mailbox of a KNAW employee and used that account to send phishing emails to contacts listed in it.
-
Jos Raaijmakers made it again to the “Highly Cited Researchers” list
Clarivate publishes an annual list of the top 1% most cited researchers worldwide. For the eighth year in a row, NIOO researcher Jos Raaijmakers is included.
-
Shining a light on nature – the importance of darkness
Since 2012, the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) has been conducting research into the effect of artificial light at night on our natural environment. For this research – Light on Nature – streetlights have been installed at four locations in the Veluwe and one location in Drenthe. Since then, they have been lit year-round from sunset to sunrise. Various institutes, universities and organisations are using these streetlights to measure the effects on different species groups.
-
Arctic-bound birds can still keep up with climate change – for now
As climate change drives earlier spring conditions in the Arctic, birds species that travel there to breed there are under pressure to migrate faster. A new study led by researchers from the University of Amsterdam and the Netherlands Institute of Ecology reveals that many Arctic-breeding waterfowl still have some flexibility when it comes to speeding up their migrations. However, this strategy may only work for a limited time.
-
Celebrating the first World Lake Day with water research & water news
"We celebrate all things that lakes do for us and spotlight the problems of pollution, climate change and biodiversity loss that threaten their ecological integrity," states Suzanne McGowan, NIOO's department head of Aquatic Ecology on the first UN World Lake Day.
-
Does north-south adaptation of animals also protect against climate change?
‘Can animal populations adapt to climate change by becoming genetically similar to more southerly populations?’ That is the question posed by ecologist Natalie van Dis. Knowledge about this could indicate which populations are most at risk from the changing climate. She has been awarded a Veni grant from NWO to investigate this at NIOO over the next three years.
-
Adapting to heat stress helps against heavy metals
Small aquatic organisms called rotifers have been found to also become tolerant to copper pollution after adapting to rising temperatures. Interestingly, the reverse is not true. An evolutionary experiment led by the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) shows this today in the journal Global Change Biology. ‘Understanding such long-term hereditary consequences of stress is crucial for informed environmental management and nature restoration.’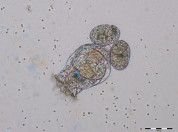
-
Soil ecology runs deep
For a long time, the soil was the domain of chemistry and physics. This only changed forty years ago. Then attention also started to be paid to the biology and ecology of soils. Today, the soil has become a large and indispensable field of research. The Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) has been uncovering the role of soil life for a healthy underground and aboveground ecosystem for several decades. Soil life also contributes to nature restoration, for example through soil transplantation and tackling invasive plants.
-
Under the bird ring's spell
Ringing of wild birds has become indispensable as a research method to track individual birds. Since 1911, some 16 million birds have been fitted with a metal ring in the Netherlands. What has that brought in terms of knowledge, protection and policy? And what do new tracking techniques add? We dive into the world of meadow birds, goose visits and infectious diseases.
-
Funding granted to create SMART experimental hub for aquatic processes
A consortium for aquatic research facilities has received funding from the Dutch Research Council (NWO) programme for large research infrastructure consortia.
